Lab 2: Init Containers
Init containers are specialized containers that run before or after app containers in a Pod. They can contain utilities or setup scripts not present in an app image.
Init containers are exactly like regular containers, except:
-
Init containers always run to completion.
-
Each init container must complete successfully before the next one starts.
-
If you specify multiple init containers for a Pod, Kubelet runs each init container sequentially.
-
If a Pod’s init container fails, Kubernetes repeatedly restarts the Pod until the init container succeeds.
-
Init containers support all the fields and features of app containers, including resource limits, volumes, and security settings, however they do not support lifecycle, livenessProbe, readinessProbe, or startupProbe for obvious reasons.
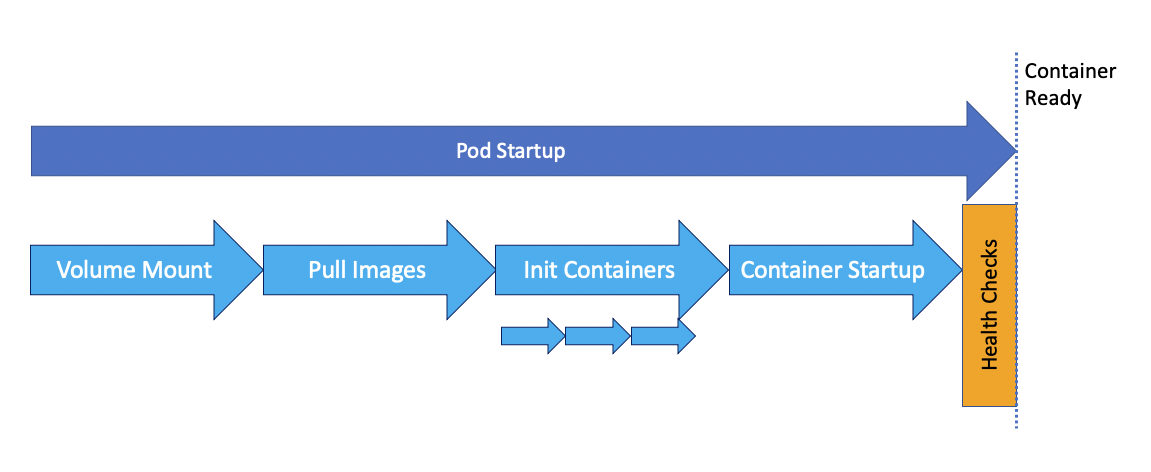
Init Containers Applied
-
Run a standard nginx container
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: nginx-demo namespace: default labels: app: nginx-demo spec: selector: matchLabels: app: nginx-demo replicas: 1 template: metadata: labels: app: nginx-demo spec: containers: - name: nginx image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent ports: - containerPort: 80``
kubectl apply -f ./training/initContainers/container.yaml``
-
Expose it with a service
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: nginx-demo-service spec: selector: app: nginx-demo ports: - protocol: TCP port: 8000 targetPort: 80 type: NodePort``
kubectl apply -f ./training/initContainers/service.yaml``
-
Open the deployment in Firefox
minikube service nginx-demo-service``
You should see the default nginx welcome page.
TODO
-
Update the deployment with the init container
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: nginx-demo-init namespace: default labels: app: nginx-demo spec: selector: matchLabels: app: nginx-demo replicas: 1 template: metadata: labels: app: nginx-demo spec: containers: - name: nginx image: nginx imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent ports: - containerPort: 80 --> Volume mapped into the nginx pod volumeMounts: - name: workdir mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html --> This container is run during pod initialization initContainers: --> Sleep for 2 Seconds - name: sleep-1 image: busybox imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent command: ['sh', '-c', 'echo sleep-1 start; sleep 2;echo sleep-1 complete;'] --> Sleep again for 2 Seconds - name: sleep-2 image: busybox imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent command: ['sh', '-c', 'echo sleep-2 start; sleep 2;echo sleep-2 complete;'] - name: install image: busybox --> Download index.html and store into work-dir command: - wget - "-O" - "/work-dir/index.html" - http://kubernetes.io volumeMounts: - name: workdir mountPath: "/work-dir" dnsPolicy: Default volumes: - name: workdir emptyDir: {}``
To initialize nginx with some content:
- We create a local volume (work-dir)
- This volume is mapped into the nginx container path (/usr/share/nginx/html) where nginx serves static HTML content from
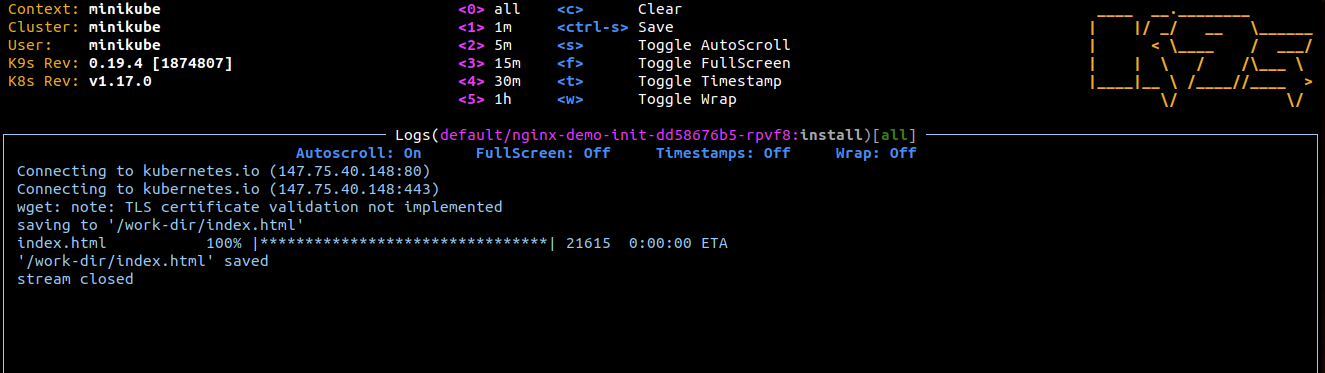
- An init container (install) that downloads the index.html file from the official Kubernetes webpage and stores it into the volume
kubectl apply -f ./training/initContainers/init-container.yaml`
-
Refresh the page in Firefox
You should see the Kubernetes page that has been downloaded by the init container.
Init Containers Examined
Now let’s have a look at what has happened in the background.
-
Start
k9sand select the nginx-demo-init Pod and hit enter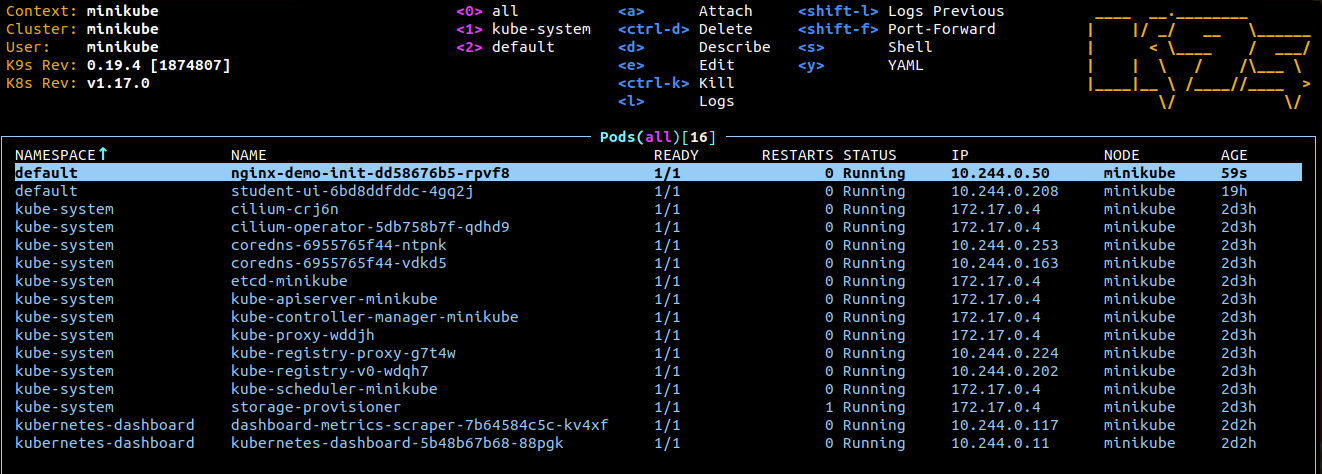
-
Select the install Container and hit enter
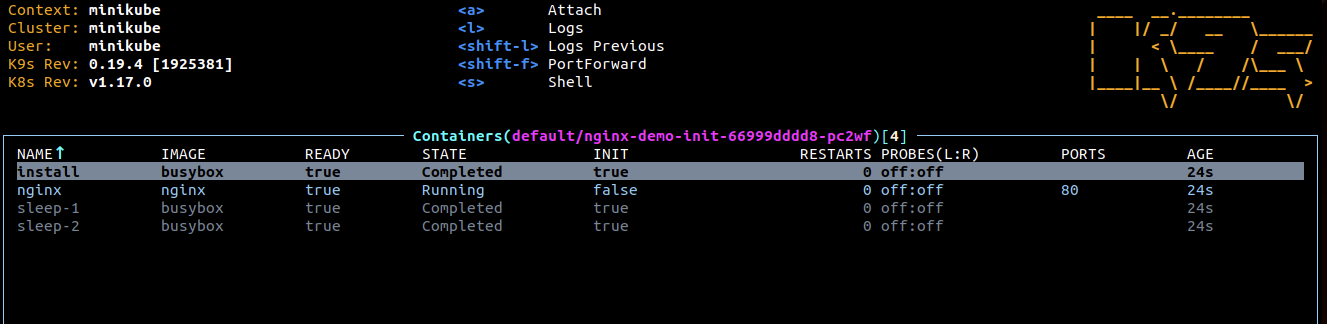
-
You can see that the shell command has downloaded the html code into the work-dir volume.
-
Hit
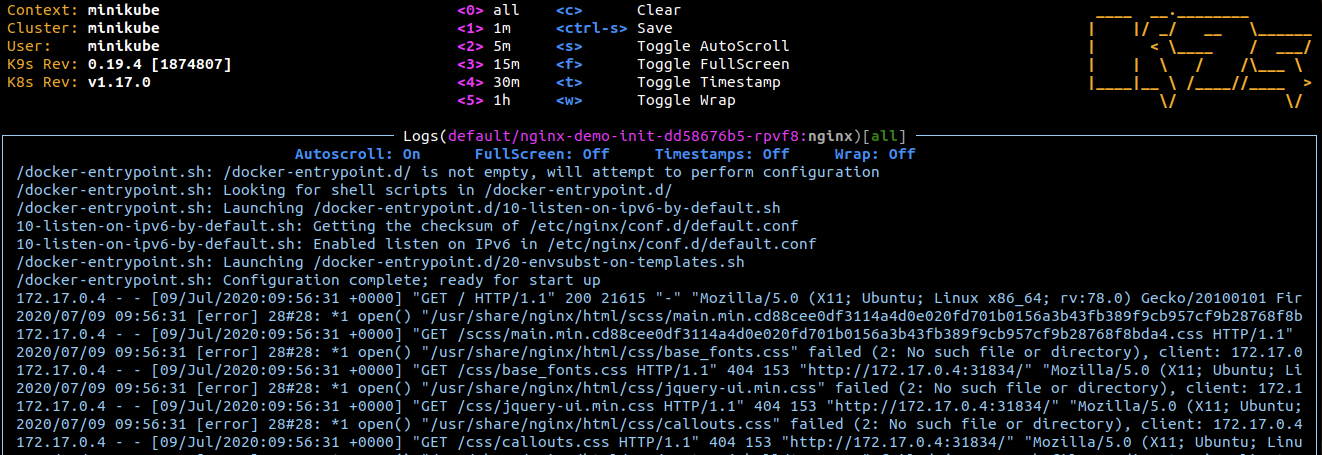
ESCto go back and select the nginx Container and hit enter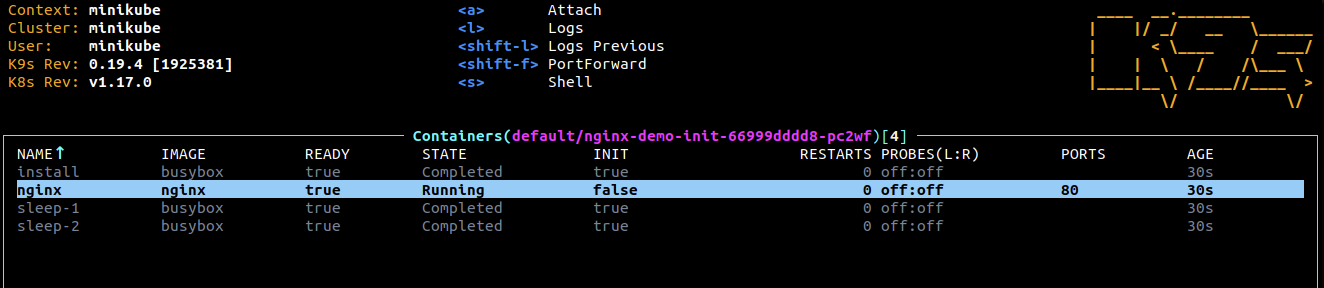
-
Nginx is serving the index.html page from the work-dir volume.
-
If you go back with
ESCyou can also have a look at how the two other containers have slept ;-)
-
Quit k9s by hitting
Ctrl-Cseveral times
Congratulations!!! This concludes the Lab on Init Containers