Lab 3: RBAC Tooling
Rakkess
Have you ever wondered what access rights you have on a provided kubernetes cluster? For single resources you can use kubectl auth can-i list deployments, but maybe you are looking for a complete overview? This is what rakkess is for. It lists access rights for the current user and all server resources.
You can get more details here.
-
Install Rakkess
curl -LO https://github.com/corneliusweig/rakkess/releases/download/v0.4.4/rakkess-amd64-linux.tar.gz \ && tar xf rakkess-amd64-linux.tar.gz rakkess-amd64-linux \ && chmod +x rakkess-amd64-linux \ && sudo mv -i rakkess-amd64-linux $GOPATH/bin/rakkess``
-
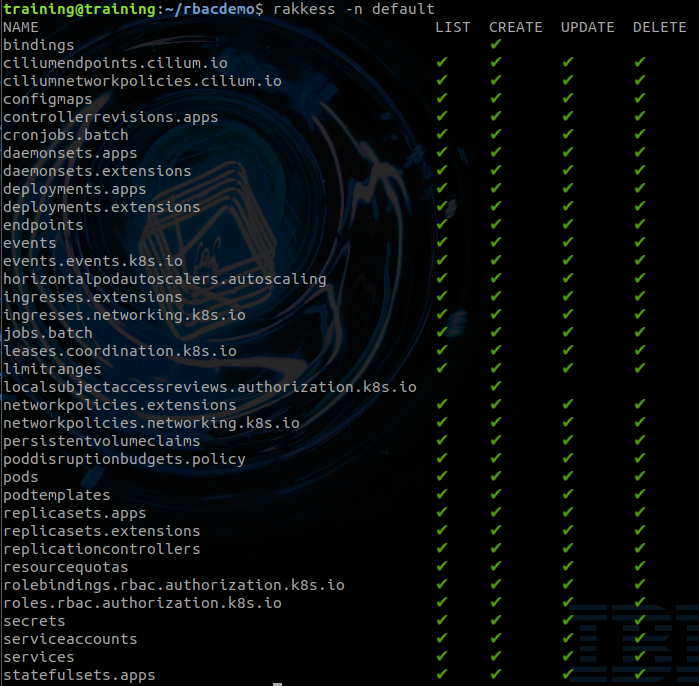
Let’s examine the RBAC for the default Namespace:
rakkess -n default``
-
And now the RBAC for the ServiceAccount that we have created earlier:
rakkess --sa service-account-1 -n default``
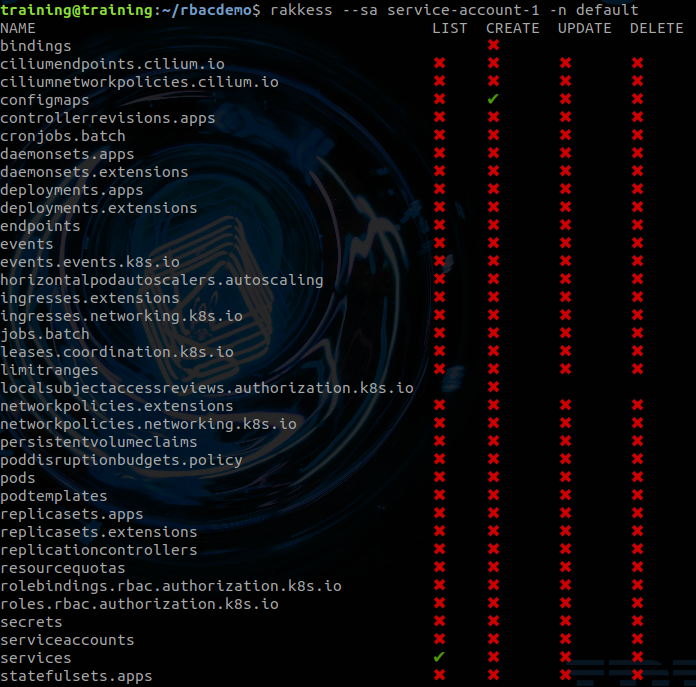
We can see that the
ServcieAccounthas the rights to listServicesand to createConfigMaps. This corresponds to theapi-roleRolethat we have defined earlier:... - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["services"] verbs: ["get", "list"] - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["configmaps"] verbs: ["create"] ...
rbac-view
Polaris runs a variety of checks to ensure that Kubernetes pods and controllers are configured using best practices, helping you avoid problems in the future.

You can get more details here.
-
Install rbac-view
#Linux wget https://github.com/jasonrichardsmith/rbac-view/releases/download/v0.2.1/rbac-view.v0.2.1.linux.tar.gz tar xf rbac-view.v0.2.1.linux.tar.gz chmod +x ./bin/linux/rbac-view sudo mv -i ./bin/linux/rbac-view $GOPATH/bin/rbac-view #Mac wget https://github.com/jasonrichardsmith/rbac-view/releases/download/v0.2.1/rbac-view.v0.2.1.darwin.tar.gz tar xf rbac-view.v0.2.1.darwin.tar.gz chmod +x ./bin/darwin/rbac-view sudo mv -i ./bin/linux/rbac-view /usr/local/bin/rbac-view``
-
Run the following in your Terminal:
rbac-view > INFO[0000] Getting K8s client > INFO[0000] serving RBAC View and http://localhost:8800``
-
Open the followin URL in your browser: http://localhost:8800
-
Rbac-view will then run some initialization which may take some time.
> INFO[0000] Getting K8s client > INFO[0000] serving RBAC View and http://localhost:8800 ... > INFO[0039] Building full matrix for json > INFO[0039] Building Matrix for Roles > INFO[0039] Retrieving RoleBindings > INFO[0039] Building Matrix for ClusterRoles > INFO[0039] Retrieving ClusterRoleBindings > INFO[0039] Retrieved 49 ClusterRoleBindings > INFO[0039] Retrieving ClusterRole system:volume-scheduler > INFO[0039] Retrieving ClusterRole system:controller:horizontal-pod-autoscaler > INFO[0039] Retrieving ClusterRole system:controller:generic-garbage-collector > INFO[0039] Retrieving ClusterRole system:controller:job-controller > INFO[0039] Retrieving ClusterRole cilium ... > INFO[0048] Retrieving Role system:controller:bootstrap-signer in namespace kube-public > INFO[0048] Retrieving Role kubernetes-dashboard in namespace kubernetes-dashboard > INFO[0048] Retrieving Role deployment-manager in namespace rbactest > INFO[0051] Built Matrix for Roles > INFO[0051] Matrix for json built``
-
Enter
clusterin theSearchRolesfield and examine thecluster-adminRole. The*means that it has all access rights to all ressources with all verbs.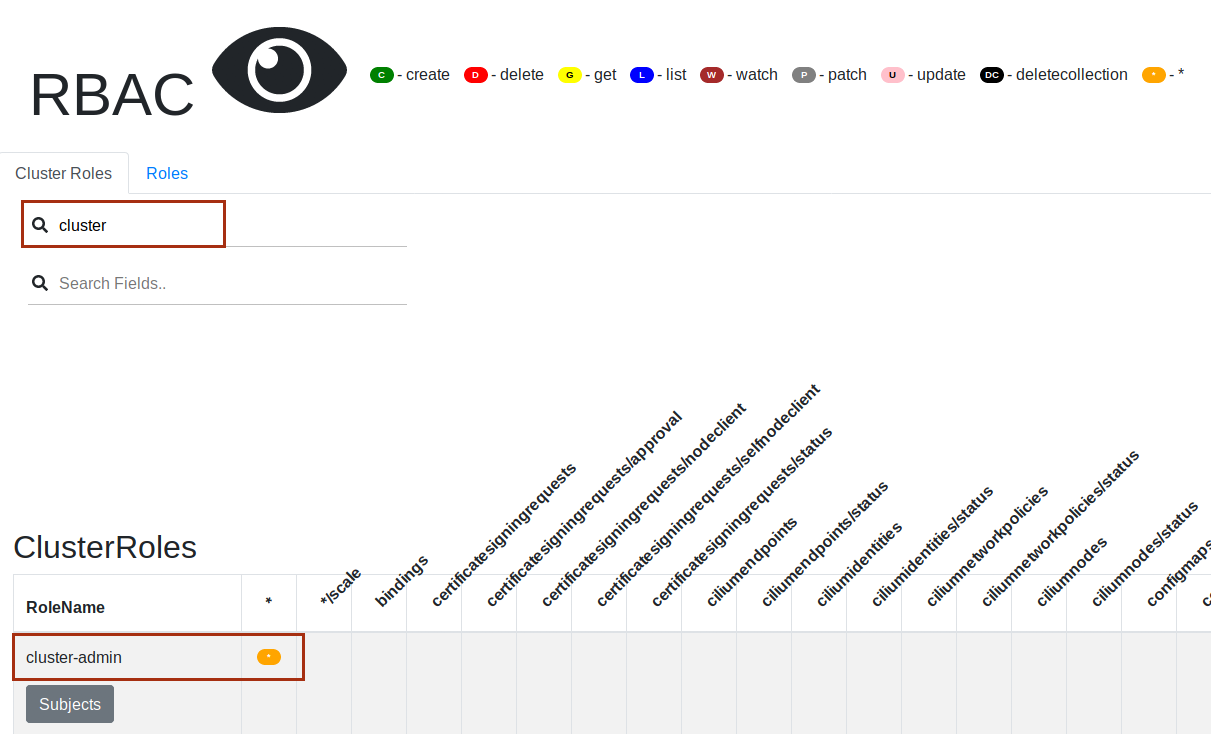
-
Switch to the Roles tab and enter
api-rolein theSearchRolesfield and examine it. We can see the access rights previously discussed, notablygetandlistrights toServices.
-
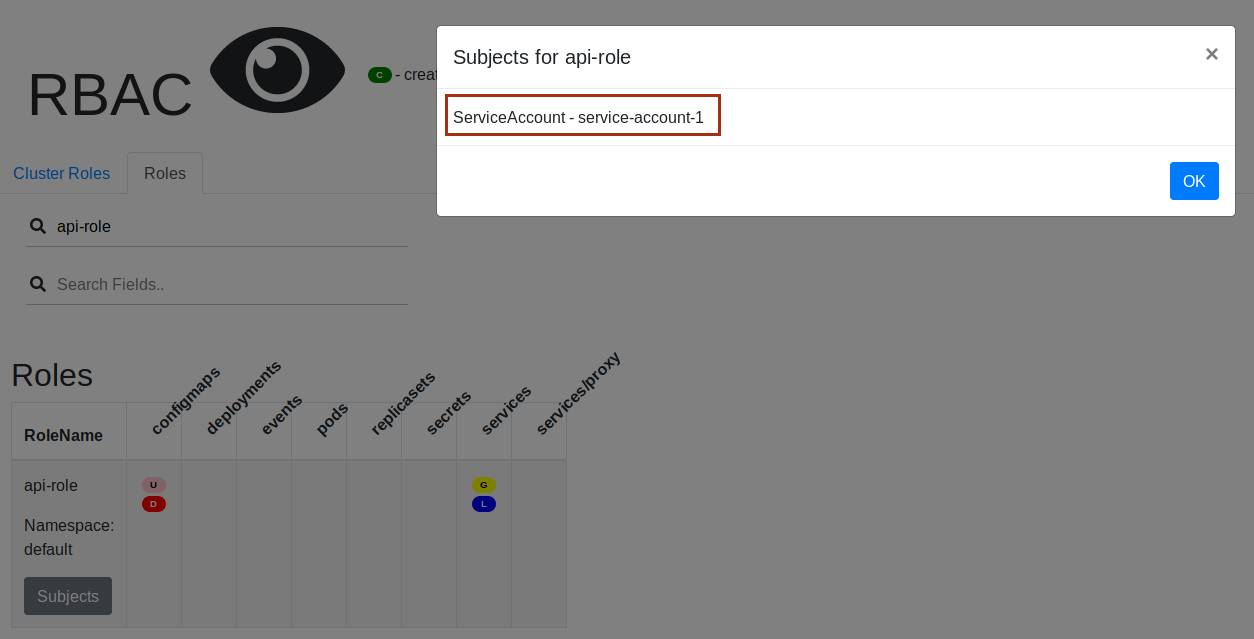
When you click on the Subjects button you will get the list of Subjects for this
Role. In this cas we can see theServiceAccountservice-account-1that is a subject of the Role.